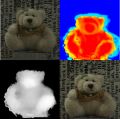
스테레오 영상은 두 대 이상의 카메라를 이용하여 얻은 영상을 말합니다. 영상을 획득한 카메라의 기하정보를 안다면 스테레오 영상에서 물체까지의 거리영상을 구할 수 있습니다. 거리영상은 컴퓨터비전에서 매우 중요한 3차원 정보를 가지고 있어 물체인식 및 추적, 3차원모델링, 로봇비전 등에 유용하게 사용될 수 있습니다.
School of Electronics Engineering, Kyungpook National University, South Korea
스테레오 영상은 두 대 이상의 카메라를 이용하여 얻은 영상

스테레오 영상은 두 대 이상의 카메라를 이용하여 얻은 영상을 말합니다. 영상을 획득한 카메라의 기하정보를 안다면 스테레오 영상에서 물체까지의 거리영상을 구할 수 있습니다. 거리영상은 컴퓨터비전에서 매우 중요한 3차원 정보를 가지고 있어 물체인식 및 추적, 3차원모델링, 로봇비전 등에 유용하게 사용될 수 있습니다.
입체카메라 또는 입체 TV기술은 차세대 컴퓨터 및 방송기술의 하나로
|
|
|
물체의 거리를 측정할 수 있는 3차원 카메라를 이용하여 다시점에서 물체의
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
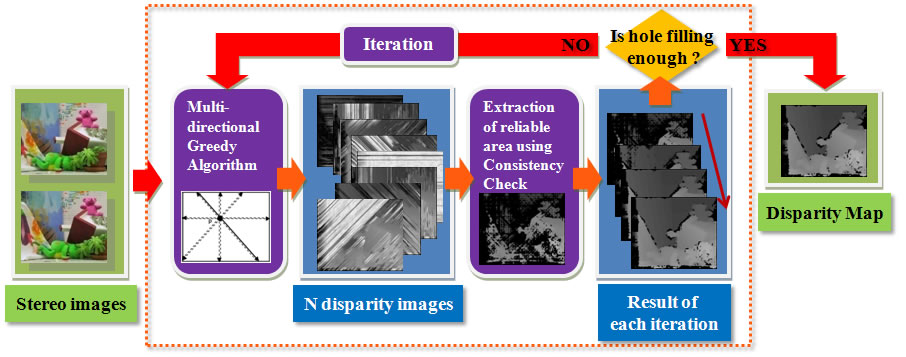
MuGSM(Multi-directional Greedy Stereo Matching)은 두 대의 카메라에서 획득한 영상으로
 |
||||
|
Fig.1 Flow of the MuGSM |
||||
| > Objects | ||||
| To obtain depth image from stereo images, we use stereo matching algorithm. | ||||
| For a long time, many stereo matching algorithms have been developed. | ||||
| And the performance are improving. But algorithms have weak points. | ||||
| Those are long computation time, memory consuming, and scan line problem. | ||||
| To solve these problems is the objects and motives. | ||||
| We proposed an algorithm, whose accuracy is as good as SGM. | ||||
| But, the computation time is shorter, and memory usage is smaller. | ||||
| > Multi-directional Greedy | ||||
|
Make disparity maps using Greedy matching along 8 or 16 directions. |
||||
 |
 |
|||
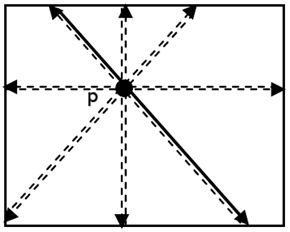
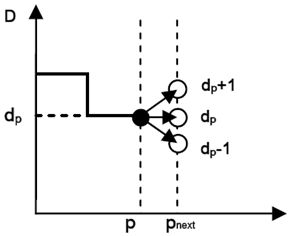
| Fig 2. Matching directions | Fig 3. Range of disparity | |||
| Number of matching direction is 8 or 16. | The relation between current disparity and next disparity. | |||
| > Consistency Check | ||||
| Find reliable area from greedy results using consisteny check. | ||||
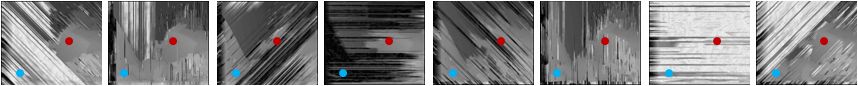 |
||||
| Fig 4. Results of each greedy matching through 8 matching directions | ||||
| Red point and blue point at each result mean same position of the original image. | ||||
 |
||||
| Fig 5. Consistency check | ||||
| Red points : The rate of inlier is higher than Consistency_ratio. | ||||
| Blue points : The rate of inlier is smaller than Consistency_ratio. | ||||
| > Iterative Expansion | ||||
| 1) After first ‘Consistency check’ get the reliable area | ||||
| 2) Restart Multi-directional Greedy Matching using reliable area. | ||||
| 3) Consistency check for the result of process 2. | ||||
| 4) Only in the holes(unreliable area), Iterate processes(2~3) are executed. | ||||
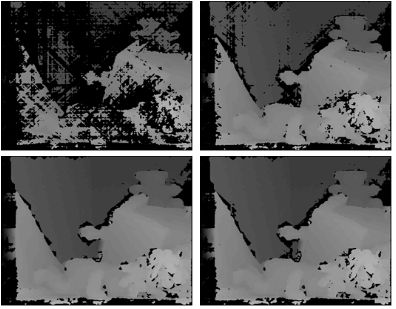 |
||||
| Fig 6. results of 1st iteration, 2nd iteration, 3th iteration, 4th iteration (from left-top, clockwise) | ||||
| > Result | ||||
| Computation time is 2~3 times faster than SGM’s. Memory usage is about 33% comparing to SGM’s. Accuracy almost equal. | ||||
 |
||||
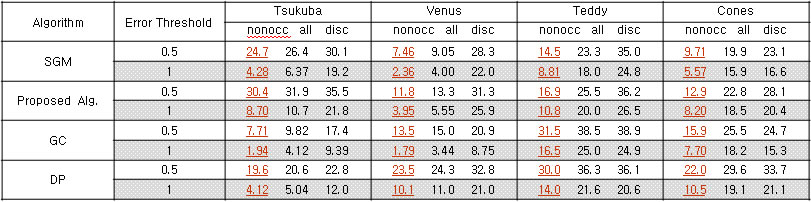
| Table 1. Compare with other stereo algorithms | ||||
 |
||||
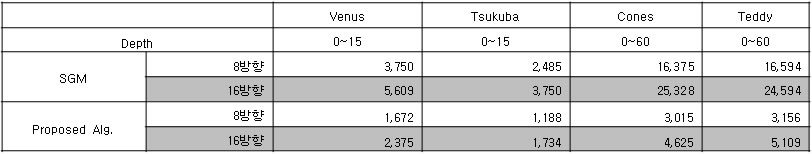
| Table 2. Memory usage | ||||
 |
||||
| Table 3. Computation time | ||||
 |
||||
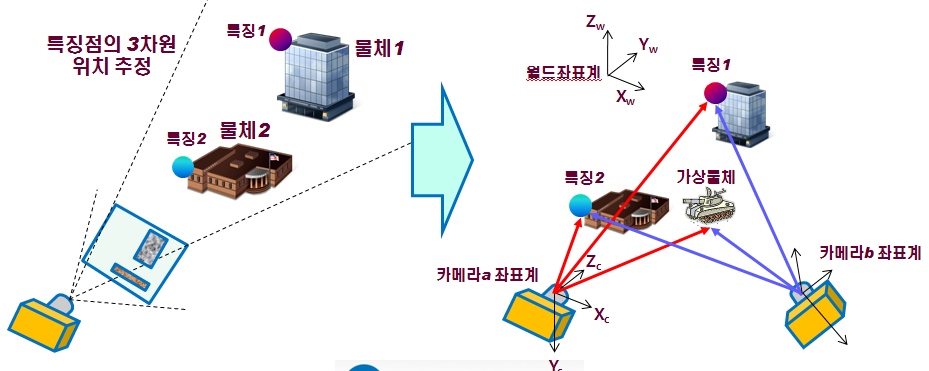
증강현실(Augmented Reality)은 3차원 가상물체(Virtual Object)를 비디오 영상과
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
– Virtual object in the origin: download(WMV, 29MB) |
|
휴대 가능한 거리센서를 이용하여 다시점 거리 영상을 획득함과 동시에
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
||
| – Beethoven plaster model : download(avi, 26.1MB) – Budda statue : download(avi, 46.6MB) |
||
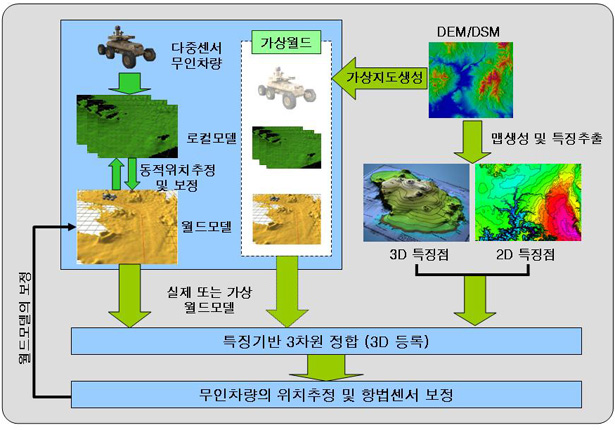
3차원 비전 기술을 이용한 무인이동로봇의 위치인식기술
| 3차원 비전 기술을 이용한 무인이동로봇의 위치인식(Localization)기술을 연구하고 있습니다. 로봇이 스스로 주행하기 위해서는 자신의 위치를 정확히 추정할 필요가 있습니다. 본 연구에서는 360도 레이저 거리정보와 3차원 지형정보 (DSM)을 등록하여 로봇의 위치를 추정합니다. 로봇의 주행 속도를 높이기 위하여 3차원 위치추정을 실시간으로 구현하고 있습니다. | |
 |
|
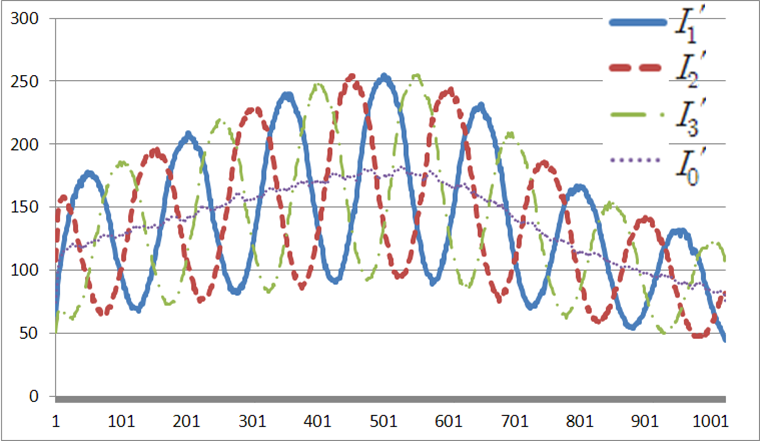
초소형 시스템을 이용하여 기존 구조광 기반의 위상 변위 방식 3차원 복원 알고리즘을 적용했을 때
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
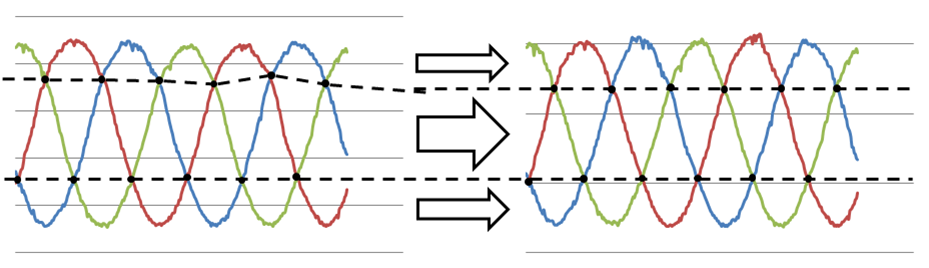 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
| ICP 알고리즘으로 정합 후 보정 전과 보정 후의 결과 비교
|
|
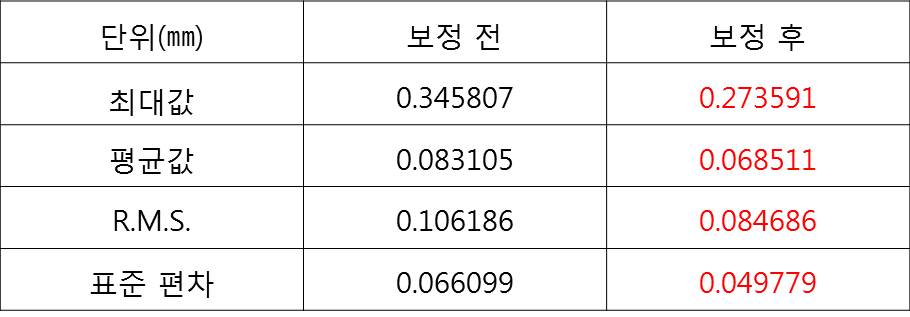 |
|
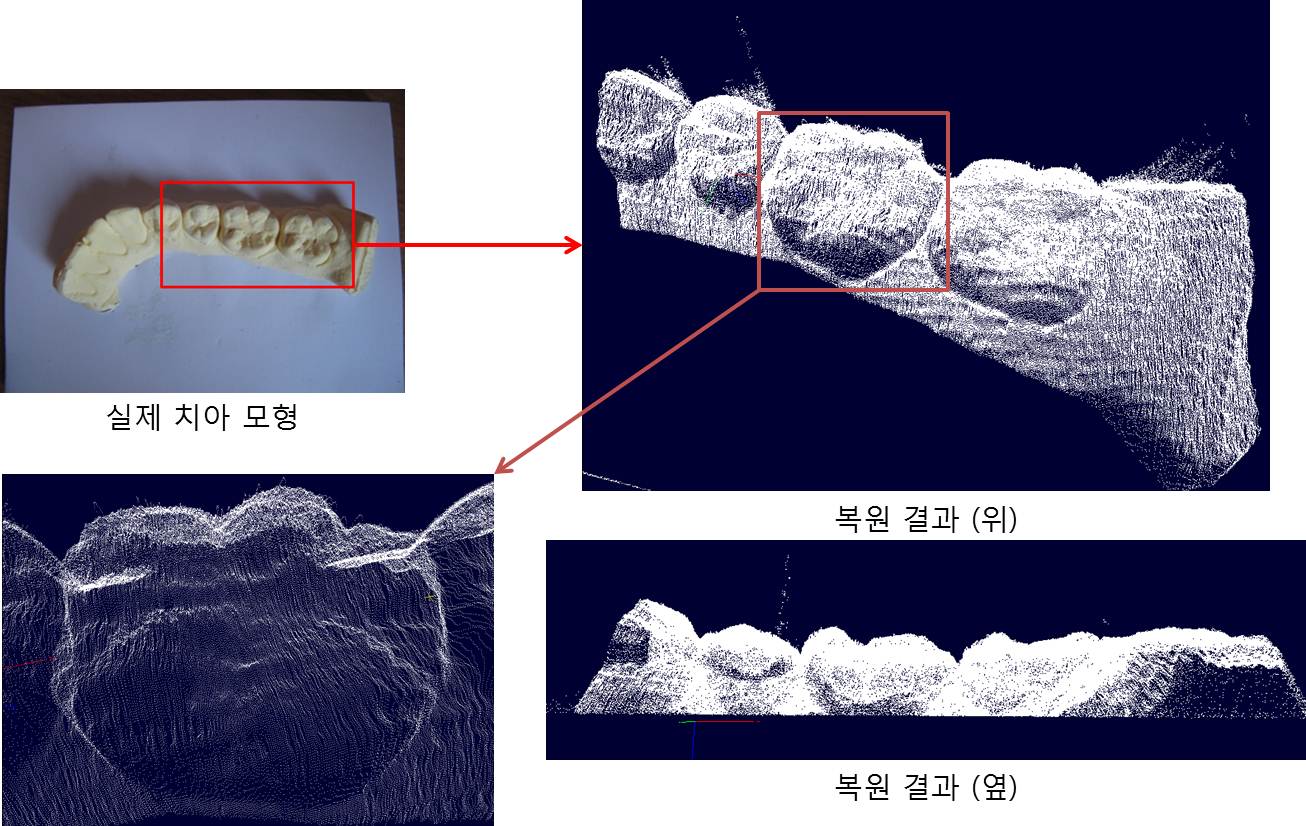 |
|
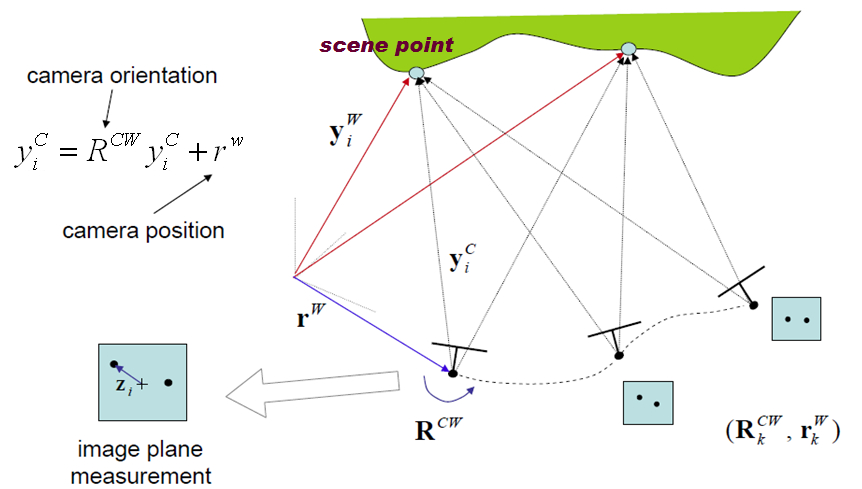
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) is a technique
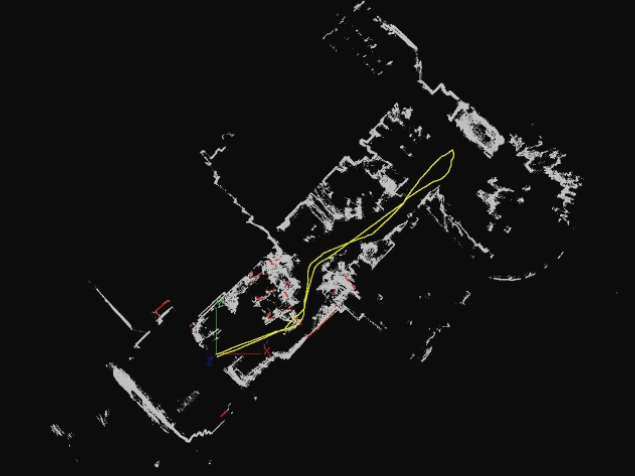
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
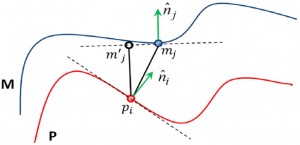
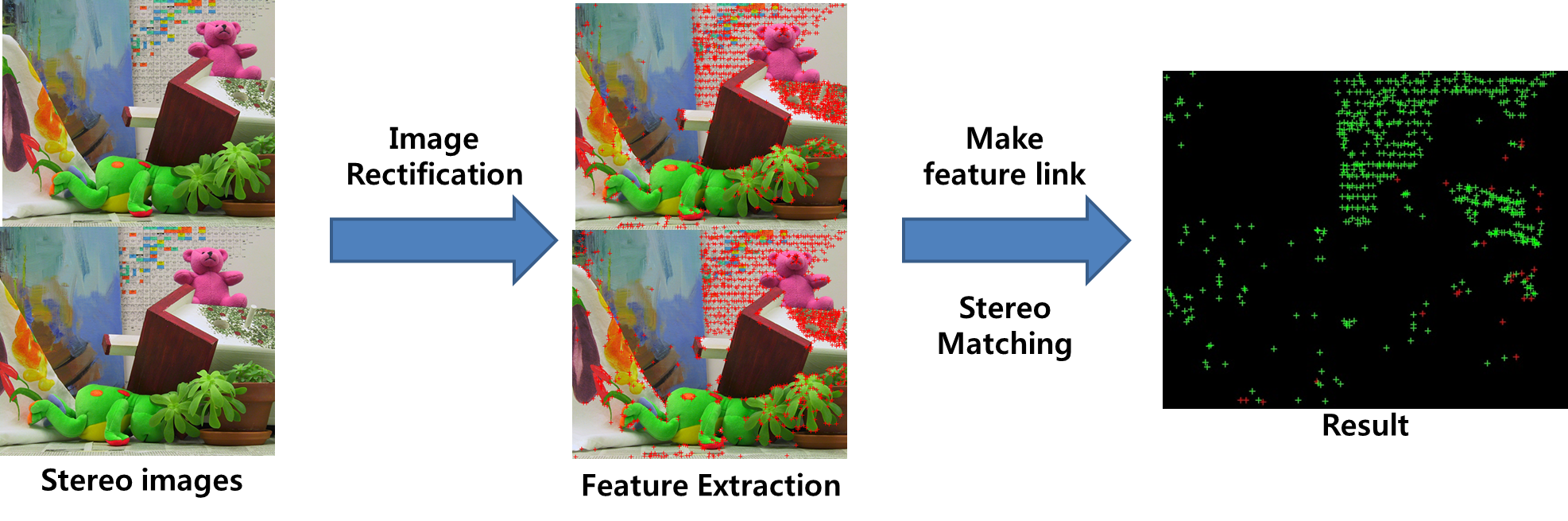
스테레오 비전 분야에서 특징 기반 스테레오 정합 방법은 빠른 수행 시간과 높은 정확성을 갖습니다.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Distance between adjacent other features. Stereo matching at same distance
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|