Abstract
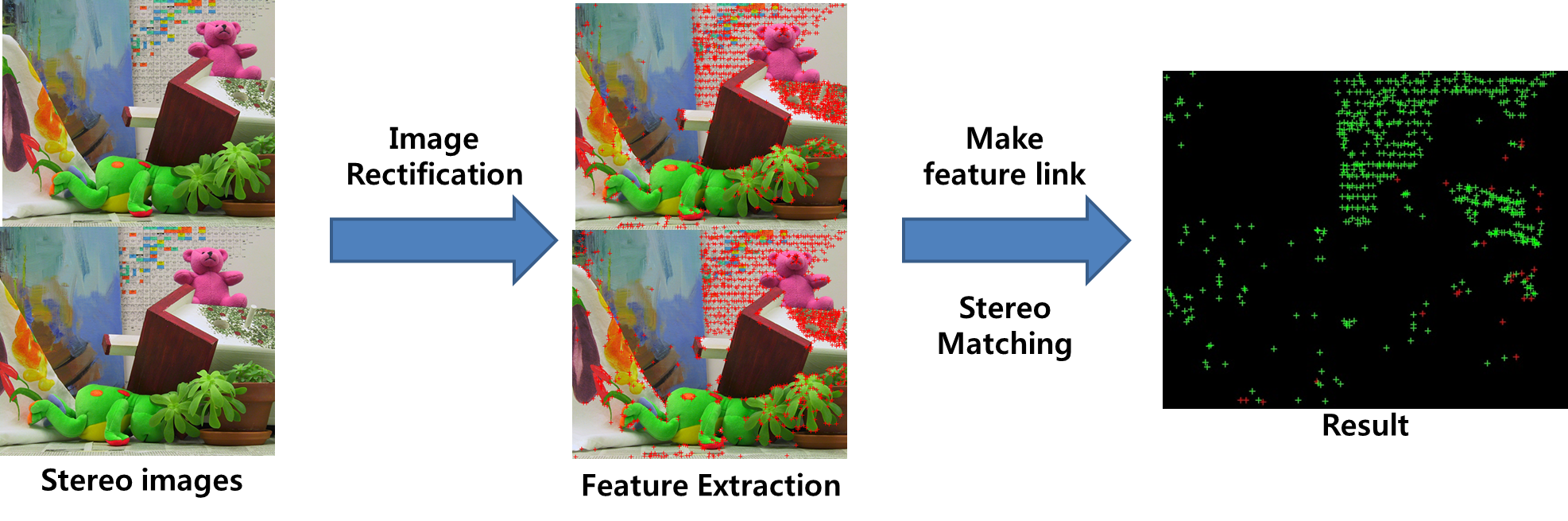
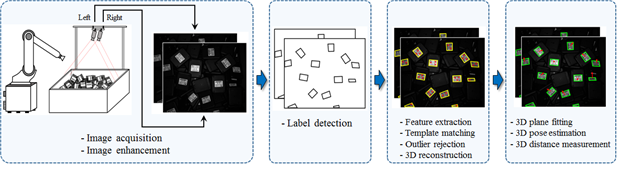
In the field of computer vision and robotics, bin picking is an important application area in which object pose estimation is necessary. Different approaches, such as 2D feature tracking and 3D surface reconstruction, have been introduced to estimate the object pose accurately. In this research, we propose a new approach where we can use both 2D image features and 3D surface information to identify the target object and estimate its pose accurately. First, we introduce a label detection technique using Maximally Stable Extremal Regions (MSERs) where the label detection results are used to identify the target objects separately. Then, the 2D image features on the detected label areas are utilized to generate 3D surface information. We calculate the 3D position and the orientation of the target objects using the information of the 3D surface.
Overview of the proposed method
Experiment result
|
(a)
(b) 충전 크래들 라벨의 자세추정 결과 (a) 라벨 위치 및 자세 정보 (b) 3차원 뷰어로 본 결과 |
(a)
(b) 여행용 어댑터 인식 결과 (a) 라벨 위치 및 자세 정보 (b) 3차원 뷰어로 본 결과 |
Integrated video